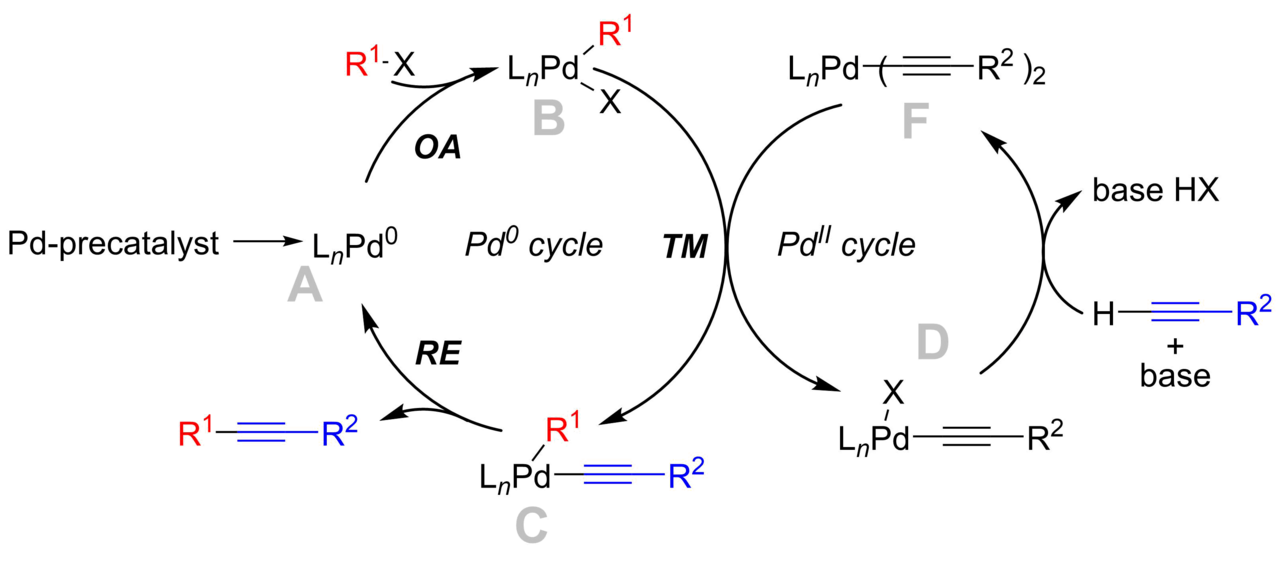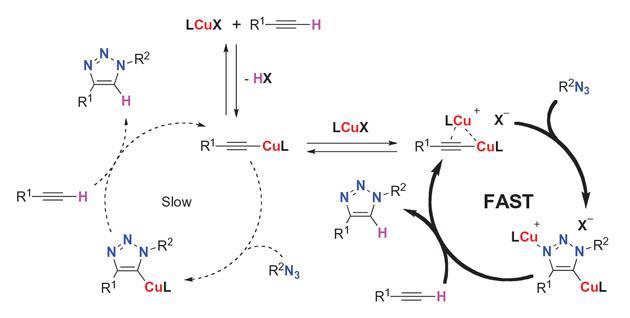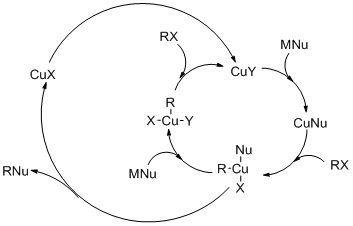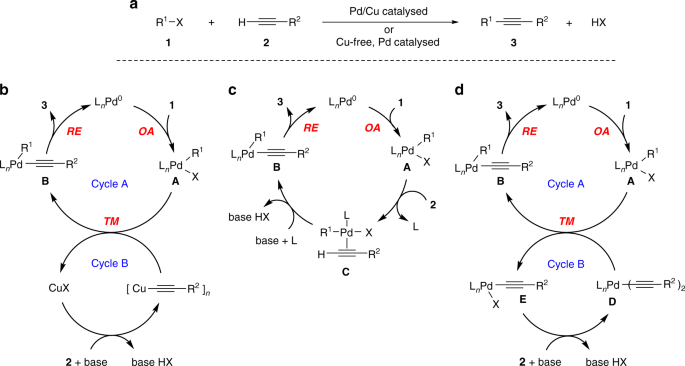
Mechanism of copper-free Sonogashira reaction operates through palladium-palladium transmetallation | Nature Communications

Direct Evidence of a Dinuclear Copper Intermediate in Cu(I)-Catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Cycloadditions | Science

Mechanism of Copper(I)/TEMPO-Catalyzed Aerobic Alcohol Oxidation | Journal of the American Chemical Society
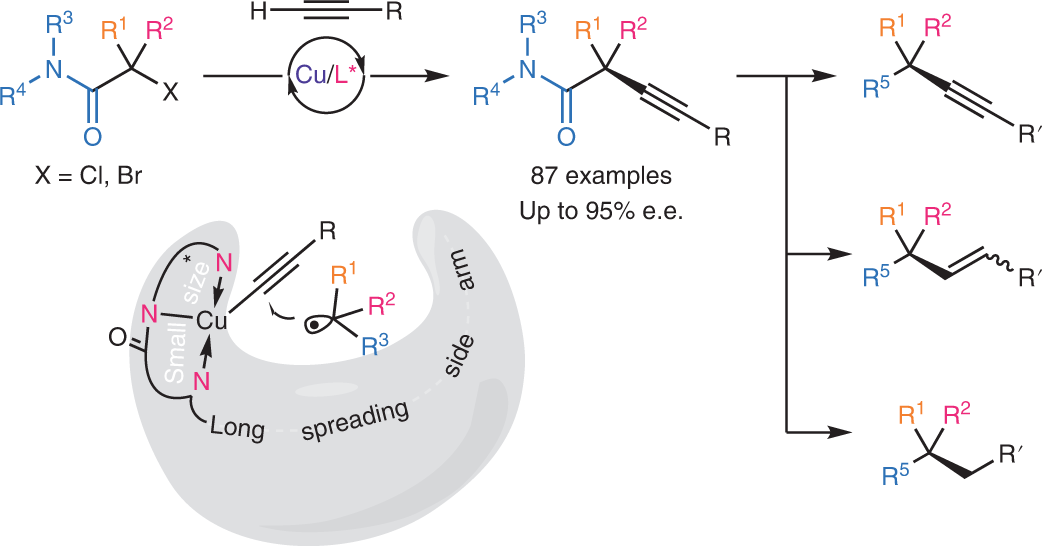
Mechanism-based ligand design for copper-catalysed enantioconvergent C(sp3)–C(sp) cross-coupling of tertiary electrophiles with alkynes | Nature Chemistry

The mechanism of transition-metal (Cu or Pd)-catalyzed synthesis of benzimidazoles from amidines: theoretical investigation - Dalton Transactions (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/C4DT01944J
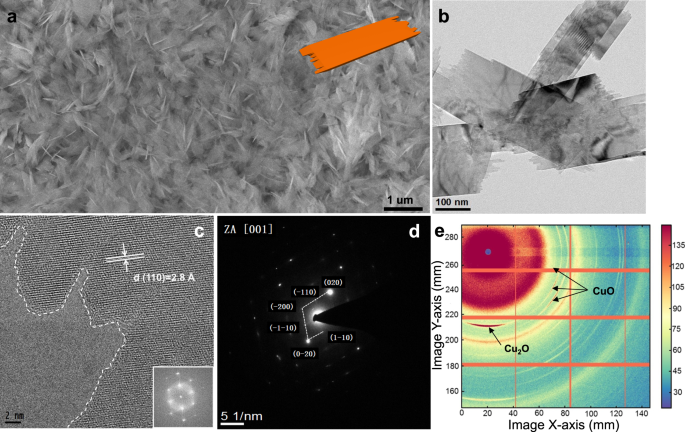
Morphology and mechanism of highly selective Cu(II) oxide nanosheet catalysts for carbon dioxide electroreduction | Nature Communications

Enhanced reactivity and mechanisms of copper nanoparticles modified green rust for p-nitrophenol reduction - ScienceDirect

Real‐time Monitoring Reveals Dissolution/Redeposition Mechanism in Copper Nanocatalysts during the Initial Stages of the CO2 Reduction Reaction - Vavra - 2021 - Angewandte Chemie International Edition - Wiley Online Library

Scheme 6. Plausible reaction mechanism. The Cu(I)-assisted cleavage of... | Download Scientific Diagram
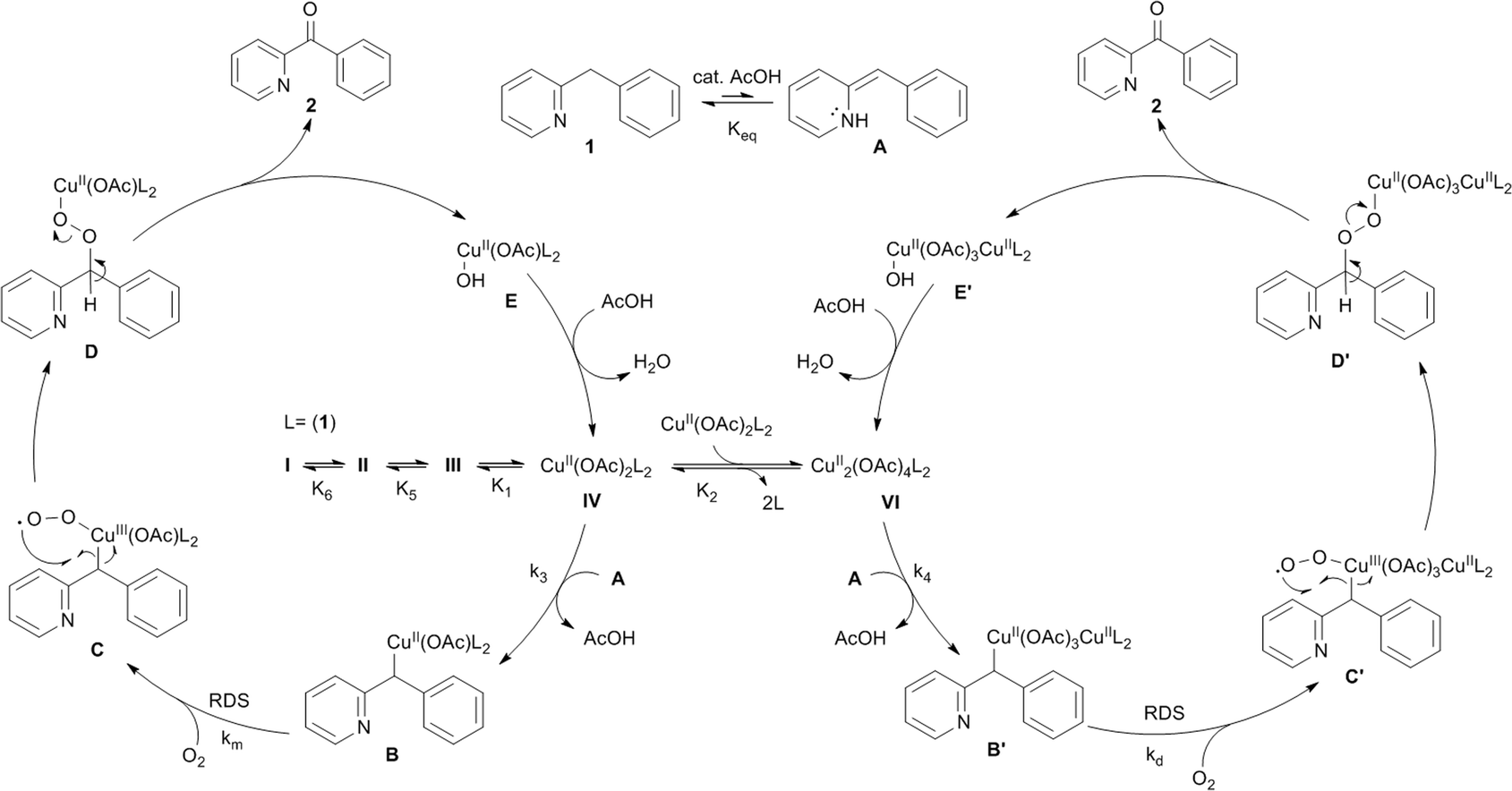
Mechanism of the Cu II -catalyzed benzylic oxygenation of (aryl)(heteroaryl)methanes with oxygen - Chemical Science (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/C5SC03530A

Proposed mechanism: L5:Cu(OTf) 2 -catalyzed Friedel-Craft alkylation of... | Download Scientific Diagram
![Understanding the mechanism and regioselectivity of the copper( i ) catalyzed [3 + 2] cycloaddition reaction between azide and alkyne: a systematic DF ... - RSC Advances (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/C7RA10653J Understanding the mechanism and regioselectivity of the copper( i ) catalyzed [3 + 2] cycloaddition reaction between azide and alkyne: a systematic DF ... - RSC Advances (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/C7RA10653J](https://pubs.rsc.org/image/article/2018/RA/c7ra10653j/c7ra10653j-f2_hi-res.gif)
Understanding the mechanism and regioselectivity of the copper( i ) catalyzed [3 + 2] cycloaddition reaction between azide and alkyne: a systematic DF ... - RSC Advances (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/C7RA10653J

A General Mechanism for the Copper- and Silver-Catalyzed Olefin Aziridination Reactions: Concomitant Involvement of the Singlet and Triplet Pathways | Journal of the American Chemical Society

Schematic representation of the Cu/ZnO catalytic mechanism for methanol... | Download Scientific Diagram

Unraveling the Reaction Mechanism of Mo/Cu CO Dehydrogenase Using QM/MM Calculations | ACS Catalysis

Mechanism of Standard NH3–SCR over Cu-CHA via NO+ and HONO Intermediates | The Journal of Physical Chemistry C

Probing the Catalytic Mechanism of Copper Amine Oxidase from Arthrobacter globiformis with Halide Ions* - Journal of Biological Chemistry